Program Design Tools
Program Design Tools
Different program design tools are:
Algorithm:
An Algorithm is the well-defined steps for performing a task or solving a problem. It includes a number of steps sequentially that are used to solve a problem.
Algorithm to find the sum of three numbers:
Step 1: Start.
Step 2: Read the three numbers suppose “a”, “b”, and “c” from the user.
Step 3: Declared a variable “sum”.
Step 4: sum=a+b+c;
Step 5: Display “sum “.
Step 6: Stop.
Flowchart:
Flowchart is the graphical representation of the logical sequence of steps involved in programming. Advantages of the Flowchart are:
• Flowchart is a better way of communicating the logic.
• Flowchart acts as guide or blueprint during system analysis.
• Flowchart help in debugging process.
Symbol used in Flowchart

Flowchart to find the average of three numbers:

Pseudocode:
Pseudocode is an informal language used to express the flow of a program. The programming process is a complicated one. So, one must first understand the program specification and organize the thoughts to create the program.
Differences between algorithm and flowchart
The Differences between algorithm and flowchart are:
| Algorithm | Flowchart |
|---|---|
| 1. Algorithm is the well-defined steps for performing a task or solving a problem. | 1. Flowchart is a graphical representation of the logical sequence of steps involved in programming. |
| 2. Algorithm is written in different steps. | 2. Flowchart is shown in the figure. |
| 3. Algorithm is more difficult to understand than the flowchart. | 3. Flowchart is easier to understand than the algorithm. |
Difference between system flowchart and program flowchart.
The differences between system flowchart and program flowchart are:
| System flowchart | Program flowchart |
|---|---|
| 1. System flowchart deals with the functionality of the entire system. | 1. Program flowchart deals with how the particular program works. |
| 2. It is hard to understand. | 2. It is easy to understand. |
| 3. It shows the data flow of a system. | 3. It shows the instruction flow of a program. |
Program Control Structure
It defines the order in which the program is executing.
It can be categorized as follows:
• Sequence
• Selection
• Iteration
Sequence:
Sequence structure consists of operations that will execute one after another serially.

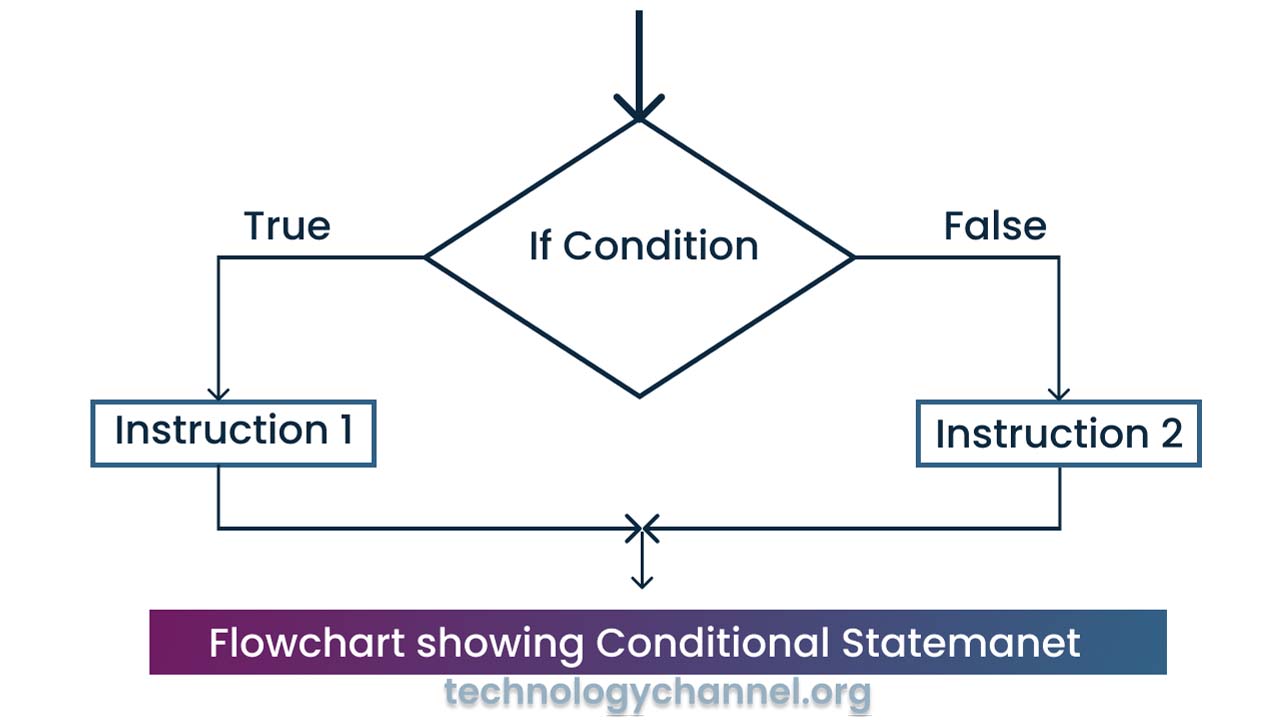
Selection/Conditional/Branching:
It helps in decision-making as it allows the operations to execute as per conditions. During execution, it gives the boolean result(true or false) and as per the result, certain operations get executed.
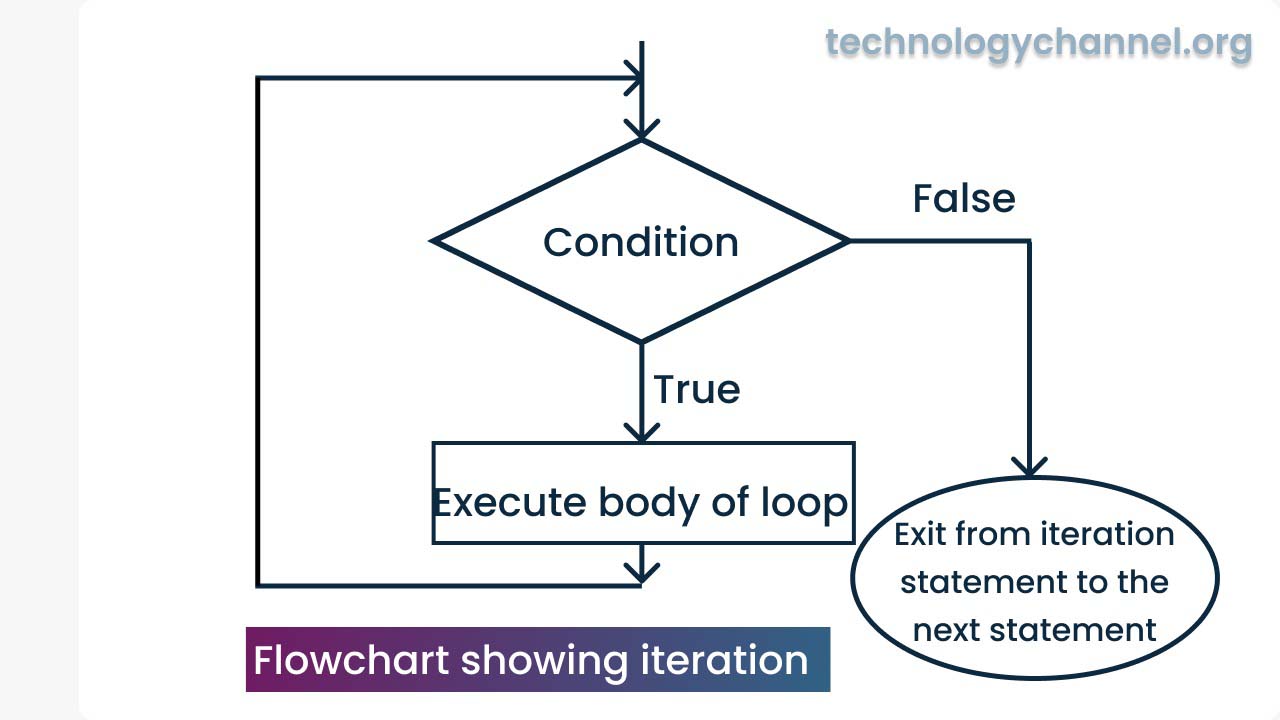
Iteration(looping):
Iteration is a control structure to repeat a specific operation a certain number of times.